- Inland Revenue draft guidance on GST groups
- Notes from the Trans-Tasman International Fiscal Association conference
As previously leaked, on Sunday Labour announced that if re-elected, it would introduce legislation to zero rate GST on fresh and frozen fruit and vegetables, with effect from 1st April next year. This is a key plank of what it’s calling its ten-point plan to address the cost of living.
According to the fact sheet supplied at the time of the launch, based on the latest statistics from the New Zealand Household Economic Survey in 2019, the policy is estimated conservatively to save households about $18 to $20 per month. Now, one of the key criticisms of this policy is of course its complexity. But Labour is confident that in defining where the boundary will lie, it will be able to draw down on overseas experience in this area. “There are boundaries everywhere in the tax system and we are confident tax officials can make it work”.
The framework around the policy is whether the fruit or vegetable has been processed or not. And processed in this context means cooked or combined with other ingredients. This therefore rules out anything canned because of the heating process that is involved. Processed does not include being cut up and wrapped without additives, so that prepared vegetables such as fresh spinach in a bag, presumably salads, would be zero rated. Similarly, mixed vegetables frozen together would be zero rated for GST. But on the other hand, the release gives an example of potatoes mashed into chips, coated in canola oil and then frozen, would be excluded and therefore still attract GST.
There is a proposal to establish a consultative expert group immediately after the election to work through the final details of the policy. One of the criticisms of the policy is, and I’ve said so previously, whether the benefit of the GST reduction would be passed through to consumers. This is to be addressed by tasking the newly established Grocery Commissioner with ensuring that supermarkets and other grocery outlets are not profiting from this change. The Grocery Commissioner has powers under the new Grocery Industry Competition Act 2023 to require it to request information and reports from supermarkets on matters such as their prices and margins.
Depreciation on commercial property to be removed, again
Labour estimates the cost of this policy to be about $2 billion over a four-year forecast period to 30th June 2028. And the sting in the tail is that this is going to be paid for by commercial property landlords. Because Labour is proposing to remove what it has called in the fact sheets, “the last remaining large COVID 19 economic stimulus measure”, which was the introduction of depreciation for non-residential buildings.
According to Treasury’s costing of the COVID 19 Response and Recovery funding decisions, that particular decision back in March 2020 costs an estimated $545 million annually. it should be said that back in 2020 when depreciation was reintroduced, there was no indication that this was going to be a temporary measure. In fact, the accompanying commentary noted:
“New Zealand’s position of a zero-depreciation rate for almost all buildings is unusual internationally. International studies have generally found buildings do depreciate. The Tax Working Group reviewed and recommended changes to these tax settings. The Government has accepted the group’s recommendation to reinstate depreciation for industrial and commercial buildings.”
So the news that barely three years after it was brought back in, it’s to be removed again will be a big surprise for the commercial property sector. And you can expect very strong representations about that. Certainly, some projects in the pipeline may be delayed as companies and investors work out the impact of the withdrawal of depreciation.
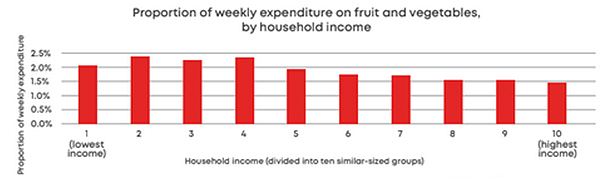
There was some interesting stuff in the accompanying fact sheet about the proportion of weekly expenditure on fruit and vegetables by household income. And what might surprise people is that it’s the lower deciles, deciles one to four, who actually spend the greatest proportion of their budget on fresh fruit and vegetables. It works out nearly 2.5% for some of the deciles. So that’s greater in relative terms than what happens for decile ten households.
But what’s also notable here is that this survey apparently shows that the amount of fruit and vegetables being purchased as a proportion of all expenditure has been declining for some time, and it declined from just under 2% in 2013 to just over 1.7% in 2019.
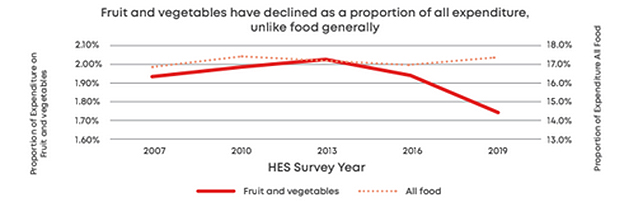
What’s happening there would be interesting to know, but it could be that the cost pressures on fresh fruit and vegetables are actually more longstanding than just the post COVID 19/climate related events burst we are experiencing at the moment. The Grocery Commissioner will obviously be paying particular attention to that on a longer term.
Increasing Working for Families support
The announcement, or the focus on the GST policy, overshadowed the other big announcement made, which was a proposal to increase the Working for Families in-work tax credit by $25 a week from 1st of April next year. This is going to provide additional support to around 175,000 low- and middle-income working families. It’s the sort of measure which is supported by many, and I would be in that group, because it’s targeted and it gives to those most in need. Although I do note that Child Poverty Action Group are still disappointed that the criteria for this is still about being in work. Their long-standing position is that the in-work criteria should be removed because that would benefit all families and particularly children of those on the lowest incomes.
The other thing that Labour’s also planning to do is to lift the Working for Families abatement threshold from its current level of $42,700 to $50,000. But that’s not going to happen until 1st April 2026. That would be worth another $13 a week to eligible families.
I’ve spoken before about what goes on with the abatement levels, and it’s worth pointing out again that when Working for Families was first introduced in 2006, the abatement thresholds were adjusted annually. That was stopped by Bill English in the 2009 Budget, with the effect that if the then threshold of $36,827 had continued to be indexed to CPI, it would now be $51,702. In that context, Labour’s promise to raise to $50,000 in three years seems a little ungenerous.
Whether yesterday’s announcements are the sum of Labour’s tax policy for the election is not yet clear. Apparently, they are. But I note that they are still promising three more cost of living policy announcements to be made during the election. So, we’ll have to wait and see.
More GST – the importance of GST groups
Moving on, Inland Revenue is presently engaged in updating its various Interpretation Statements and other guidance, such as Questions We’ve Been Asked and in various statements of practice, to update various legislative updates that have happened over time. Some of this advice refers to the Income Tax Act 1994, whereas now we’re on the Income Tax Act 2007. So, Inland Revenue has been releasing a steady stream of updated guidance for consultation, and most of these updates confirm the existing position.
The latest released last week and also continuing this week’s GST theme, are two draft interpretation statements for consultation on the treatment of GST groups. One looks at when GST groups may be formed in general, and the second looks specifically at the rules around GST groups for companies
There has been a little bit of uncertainty around how the GST group rules interacted with other parts of the GST Act, and that was taken care of by an amendment included in the Taxation (Annual Rates for 2021-22, GST and other Remedial Matters) Act in 2022, which clarified the interaction of the GST group rules with the Income Tax Act. The position now is that the GST grouping rules are applied before the other provisions in the GST Act.
The idea behind the GST grouping rules is to eliminate the need to be charging and recovering GST on intra group sales. Think of a large group that’s supplying goods and services to another group member. If they are not within the same GST group, one party would charge GST and the other party would have to recover the GST. So, the idea of the grouping rules is to simplify administration.
How it’s done is that there is a representative group member chosen that carries on all the group members activities and that entity, whoever it is, is responsible for all the administration of GST. If a sale is made by someone outside the GST group, to a member of the group, it’s deemed to be made to the representative member as the registered person. Similarly, the various sales that might be made by group members to outside the GST group, are all treated as taxable supplies made by the representative member.
However, taxable supplies between group members are mainly disregarded with the idea of simplifying administration. One paper considers what happens with GST groups of companies. These can be formed where there is 66% commonality of shareholders, similar to the income tax rules for loss-offsets between group companies. In some cases, you can have non-registered entities as part of the GST group. The other paper covers the rules in general and where you can have groups of other entities such as trusts, for example, or maybe limited partnerships.
So, the two papers explore that and explain the background behind how the GST group rules operate. And as I say, these are part of a wider Inland Revenue project to update its material. These are very useful Interpretation Statements and consultation on these is open until 14th of September.
At the same time, I can’t help but think that Inland Revenue should be exploring the idea of introducing compulsory zero rating of GST between all GST registered entities. This would largely eliminate the need for rules around GST grouping. I think what it would also do is tackle an area of GST fraud which incurs relatively frequently where a fraudster might register for GST and then files a number of false GST returns, claiming input tax based on made up invoices.
Although Inland Revenue tracks down and catches these people, there is a time lag while the fraud is going on. I’m beginning to think if you want to try and tackle that, compulsory zero rating between GST registered businesses is perhaps a place to start. Giving Inland Revenue more resources to look into it, is another interim measure that could be done.
Trans-Tasman Tax issues
And finally on the Thursday and Friday just gone I was at the International Fiscal Association Australia-New Zealand Joint Conference in Queenstown. This is the first time in over 30 years the Australian and New Zealand branches have held a joint conference. It was highly successful. One reason IFA conferences are so attractive is because very senior Inland Revenue, and Treasury officials, and for this conference, Australian Tax Office and Australian Treasury officials, attend and share their views on insights on current tax topics. (Consequently, the conferences are held under Chatham House rules to enable officials to speak freely).
It’s always interesting to swap notes with other attendees and this conference was no exception, but it was particularly interesting because of the focus on Australasian issues. Both sides got to see differing perspectives on common topics, which included the question of tax treaty policy and updates from very senior people from both Australia and New Zealand on the OECD Pillar One and Pillar Two proposals. Australia and New Zealand are very well represented on the key working groups on this, we’ve got very good knowledge of how things are progressing. We also got a view on the latest environmental and tax developments, including a view from the IMF’s principal environmental fiscal policy expert.
“A hot steaming mess” – the perils of Australian taxation
A particularly interesting session was on the taxation of trusts in the trans-Tasman context. the current state of Australia’s trust tax law was described as a “steaming hot mess”. I regularly encounter scenarios where trustees have migrated to Australia without considering the tax ramifications, and a steaming hot mess is perhaps an understatement of the consequences. Overall a very useful session.
Incidentally, Australia and New Zealand are currently renegotiating the double tax agreement between the two countries. And the point was made that although as tax professionals we tend to look at tax treaties solely tax related, one panelist reminded everyone that they’re actually often part of bigger trade negotiations.
For example, as part of its efforts to obtain a free trade agreement with the EU, Australia has opened negotiations with double tax agreements with several EU countries. Apparently one reason a UK a double tax agreement between the United States and the United Kingdom in the mid-1970s was so advantageous for the Americans was because at that time the UK was negotiating the purchase of upgraded missiles for its submarine fleet.
Well, that’s all for this week. I’m Terry Baucher and you can find this podcast on my website www.baucher.tax or wherever you get your podcasts. Thank you for listening and please send me your feedback and tell your friends and clients. Until next time, kia pai to rā. Have a great day.

