- Inland Revenue guidance on the new 39% trustee rate
- Briefing the Minister
- Tax credits or threshold adjustments?
The Finance Minister signed off 2023 rather like a Shortland Street season finale, leaving us all guessing as to the exact extent of the proposed tax cut package and when it might apply. We were told at the Half Year Economic Fiscal Update Mini-Budget on 20th December we could expect more details shortly. But now it’s February and we’re no wiser. It now appears likely we’ll have to wait until the Budget in May for full details.
A 39% trustee tax rate?
On the other hand, the business of government carries on and we will know early next month whether the coalition government will proceed with increasing the trustee tax rate to 39%. That’s when the Finance and Expenditure Committee reports back on the Taxation (Annual Rates for 2023-24, Multinational Tax, and Remedial Matters) Bill. This is the annual tax bill currently before Parliament which proposed the increase to 39%. It must be passed by 31st March.
The FEC heard oral submissions last week, and I note that (previous podcast guest) John Cantin thinks it’s most likely that the tax rate will go ahead. This is even though such evidence as we’ve seen suggests that a 39% tax rate for trusts probably represents over taxation of many trusts once the wider family context is considered.
I tend to agree with John that the rate increase will go ahead, in part because it is a base protection measure as it aligns the trustee rate with the top individual tax rate. But also, the Government will probably be grateful for some additional revenue to counterbalance the lost revenue from the proposed tax threshold adjustments. That said, I know a number of submissions proposed that some sort of de minimis threshold is introduced, and the rate of 39% will only apply on the excess.
Inland Revenue’s view on tax planning for the new 39% rate
Meantime, and rather helpfully, Inland Revenue released last Friday some high-level guidance about how it might perceive taxpayer transactions and structural changes ahead of a rate change. General Article GA 24/01 proposed increase in the trustee tax rate to 39% has been released in response to requests since the rate was proposed for guidance on how Inland Revenue might perceive some transactions.
GA 24/01 contains several examples of possible transactions and how Inland Revenue would view the transaction. The first example is a company owned by a trust which changes its dividend paying policy. Inland Revenue considers a company is entitled to change its dividend paying policy and while taking into account the funding needs of shareholders and applicable tax rates, it “is unlikely without more (such as artificial or contrived features) to be tax avoidance.”
The example then notes Inland Revenue might have concerns if the company could pay a dividend by crediting shareholder current accounts, but “objectively has no real ability to pay those credit balances if it was to be liquidated.” In other words, the company tries to pay a dividend ahead of the trustee rate increase but doesn’t have the funds to pay the dividends in cash in full.
Another example is of a trustee choosing to wind up a trust. Again, GA 24/01 suggests such a step is “unlikely without more (such as artificial or contrived features) to be tax avoidance.” GA 24/01 also looks at the question of trustees investing in Portfolio Investment Entities instead of other available investment options. The advantage here is that the maximum rate applicable to Portfolio Investment Entities is 28% Again, Inland Revenue concludes such a step is unlikely without artificial or contrived features to be tax avoidance.
That said, Inland Revenue is going to continue to gather information on trusts and something it has said would be of concern to it is where income is allocated to a beneficiary taxed at a lower rate, and then instead of actually being paid out or being fully available to the beneficiary, is resettled back on the trust. In effect, the beneficiary has not benefited from the distribution.
The allocation of income to a beneficiary, where the beneficiary actually doesn’t know of an allocation or has no expectation of receiving the income together with replacing dividend income with loans “in an artificial manner”, are other alternatives which would concern Inland Revenue if there’s no real commercial reality behind the arrangement. And then artificially altering the timing, ie: bringing forward or deferring any taxable deductible payment, particularly it’s linked to existing contractual terms or practise for the date of payment.
These are just a number of scenarios which might play out. And clearly Inland Revenue’s watching. As I said, we really won’t know what the state of play will be until early next month when the FEC reports back, and when it does, we’ll let you know. But as I said, the expectation I have is we should see that tax rate increase.
The Tax Principles Act may be gone but its first draft report lives on
Moving on, one of the first things the coalition government did was repeal the controversial Tax Principles Act. Nevertheless, the draft report that was due to be produced under the Tax Principles Act has been proactively released and it makes for some interesting reading.
The report gives a background as to why it’s being prepared, its reporting obligations, and it explains what are the tax principles that were measured. These were included in the Act – efficiency, horizontal equity, vertical equity, revenue integrity, compliance and administration costs, flexibility and adaptability and certainty and predictability. Incidentally, a lack of certainty and predictability was one of the objections that was made about the Tax Principles Act because didn’t go through the full generic tax policy process.
Inland Revenue was required to assess the principles, against four measurements:
- Income distribution and income tax paid;
- Distribution of exemptions from tax and of lower rates of taxation;
- Perceptions of integrity of the tax system, and
- Compliance with the law by taxpayers.
The report has lots of interesting graphs including the taxable income distribution for individuals for the 2022 tax year which shows a wee spike around the $180,000 mark.
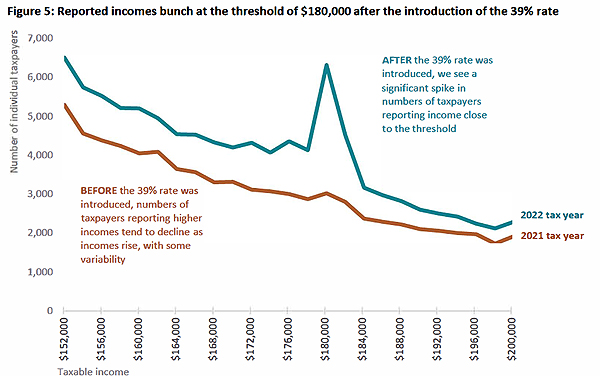
I think that’s rather revealing even if there are apparently only 4,000 individuals involved. But still for those taxpayers you may need to have a good explanation of what’s going on.
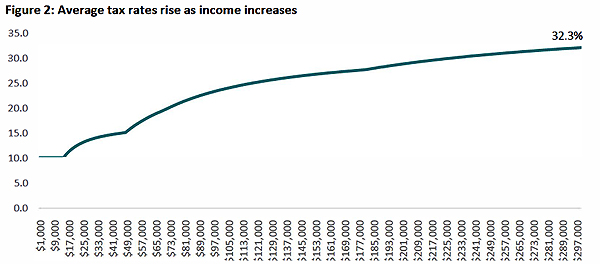
There’s a graph showing how average tax rates rise as income rises. This graph tops out at $300,000, by which point the average tax rate has risen to 32.3% for someone of that income.
But what I thought was quite interesting were the graphs looking at the average tax rates from 2012 to 2022. In particular the graphs illustrated the effect of inflation combined with the non-adjustment of thresholds. That’s an issue I’ve talked about frequently and threshold adjustments we think will be at the core of the Government’s proposed tax relief package expected to be rolled out later this year.
The report notes between 2012 and 2017, the average tax rate for the most common regularly employed worker increased by 0.1 percentage points. Not too bad. But from 2017 to 2022 it increased by 1.2 percentage points. That’s quite a more significant example. Overall, in the period between 2012 and 2017 it rises from 14.9% to 15% and then rose between 2017 and 2022 to 16.2%.
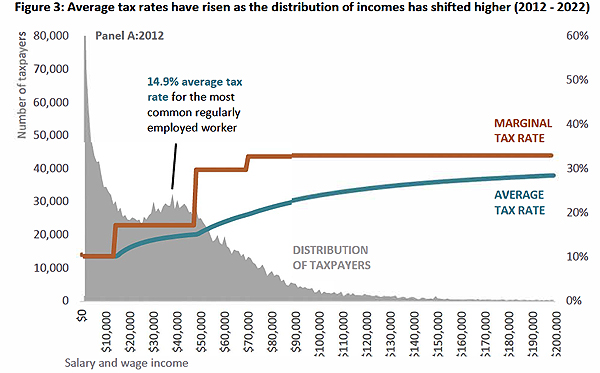
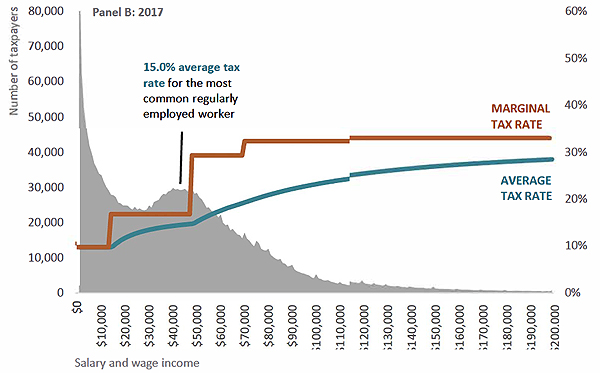
This is the fiscal drag (or bracket creep) I discussed with Susan Edmunds of Stuff. It’s been an issue for quite some time. As wages rise faster, they drag persons on average incomes into a higher tax bracket. It will be interesting to see how the Government addresses it, and I’ll talk about that in a few minutes.
There’s plenty of other material to consider. There’s an interesting stat that the top decile of taxable income earners paid 44% of personal income tax. The report notes that the same group earned 33% of total income and suggests this is a better indicator of progressivity in the tax system than the fact that 44% of tax is paid by the top decile.
The arguments will rage around the progressivity and fairness, David Seymour of the Act Party for one has been talking about this area. Overall, there’s a lot to consider in the report. Interestingly, in the note to Cabinet regarding the repeal of the Tax Principles Act, the new Minister of Revenue Simon Watts suggested that much of this data could be made separately available, perhaps as part of Inland Revenue’s annual report. I hope we do see that, because for some time I’ve felt that the discussion around bracket creep, fiscal drag and thresholds has been sort of sidelined because governments have been not too keen to discuss it in great detail.
Briefing the Minister
Mentioning the new Minister of Revenue Simon Watts, another report released last Friday was the Briefing to the Incoming Minister. I think some of the data that’s been included in this draft report under the Tax Principles Act, would normally go into the Briefing for Incoming Minister.
What I found interesting in the Briefing was Inland Revenue’s discussion around where it’s at and the effect of the completion of the Business Transformation Programme which has allowed it to “deliver significant cost savings”. For example, the Briefing notes the amount of revenue collected for the year ended 30 June 2023 grew by 62.5% compared with the year ended 30 June 2016, the last full year before transformation began. Over the same period, the number of Inland Revenue full-time equivalents reduced by 29%.
There’s been a lot of talk about government cuts for the public sector, but I think the Briefing subtly, or not too subtly, you might say, raises a good question – if an organisation has managed to reduce its headcount by 29% and its funding is not tracked with inflation since 2017, which appears to be the measure for the basis of these public spending cuts, why would you add further cuts?
My view would be, and I think I wouldn’t be alone in thinking this amongst tax practitioners, is that Inland Revenue is under a bit of strain. We know it probably needs to boost its investigations efforts. So why it should be on the chopping block when it’s already done much of what any government would want it to do – more with less. But we’ll see how that plays out.
I thought the amount of commentary in the Briefing around the question of funding this point was quite interesting. It notes that for the year, to June 2024, the department gets about $800 million a year. And at October 31st 2023 its workforce was 4,231. Whereas back in June 2016 it was 5,662. And by the way, the report also notes the department has planned for taking a $13.9 million reduction for the year to June 2025, which was announced by the previous government in August 2023.
According to the Briefing funding would be running around about $700 million going forward, but then adds something the government should probably pay attention to.
“Our primary cost pressures in out years will be remuneration and inflationary cost pressures on technology as a service contracts, accommodation, leases and other operating costs. We are currently developing options for meeting these costs and we’ll report back to you on these matters.”
I know speaking as an employer and along with other colleagues, finding staff is difficult at the moment, so that puts pressure on salaries, obviously. And Inland Revenue is not immune to that because it needs to pay near market rates to attract good quality people, because as the gamekeeper, so to speak, it needs to match the poachers on the other side. Like so much in the year ahead it will be interesting to see how the Minister settles in and what happens with Inland Revenue’s funding.
The shape of things to come – tax credits or threshold adjustments?
And finally, coming back to what lies ahead, as I mentioned at the start, the Half Year Economic Forecast Update left us none the wiser as to the nature of the threshold adjustments, which we think are going to happen. In that gap. David Seymour of ACT has come forward and talked about the ACT policy, which is to simplify the tax rate structure down from the current five rates down to three, with a top rate of 33%. This is moving back to the rate structure which applied from 1989 through to 2008. Basically, until 1 April 2000 (when the 39% rate was introduced) there were two main rates with a tax credit adjustment for low-income earners.
David Seymour talked about tax credits similar to the existing Independent Earner Tax Credit. But as I told RNZ while the concept’s not uncommon, there’s still the issue we discussed earlier. What about adjustments for inflation and keeping the true value of that, otherwise lower rate/ lower income earners will face higher effective marginal tax rates.
There’s also a certain complexity with tax credits. The thing about applying thresholds across the board to everybody, it’s pretty straightforward. Whereas with tax credits, if there’s a claim process that’s involved, not everybody will claim that. It introduces a bit of complexity at the bottom end, which Inland Revenue’s Business Transformation was determined to do the opposite in order to try and make it as easier for most taxpayers to comply.
As mentioned, we have the independent earned tax credit, but it starts cutting out at $44,000 and then drops out at $48,000 once income crosses that threshold. We’ll have to wait to see what happens and in the meantime there will be plenty of debate ahead. We will bring all of those developments to you as usual.
In the meantime, that’s all for now. I’m Terry Baucher and you can find this podcast on my website www.baucher.tax or wherever you get your podcasts. Thank you for listening and please send me your feedback and tell your friends and clients. Until next time, kia pai to rā. Have a great day.

