- OECD announces progress on the global minimum tax deal
- Phillip John Smith gets caught, again
Inland Revenue has released a draft interpretation statement on the research and developments loss tax credits regime. This is a refundable tax credit available to eligible companies when they have a loss which has arisen from their eligible research and development expenditure.
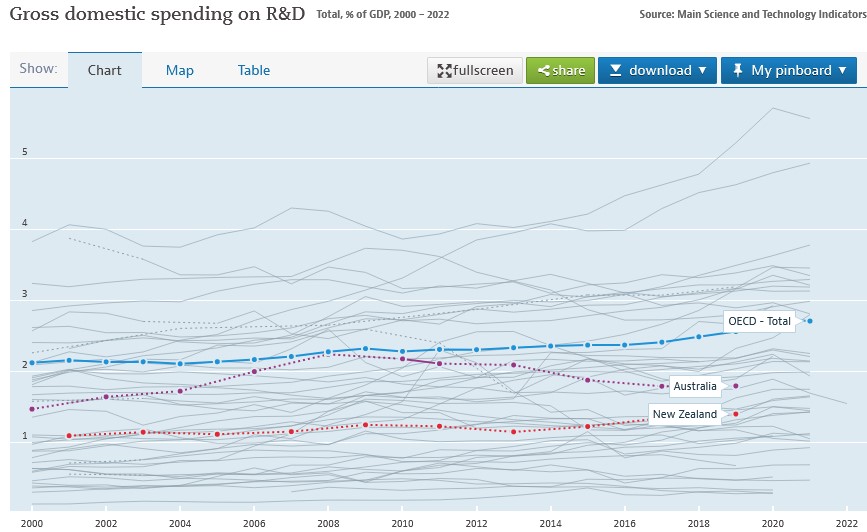
The regime was introduced in 2016 to encourage business innovation and also to address New Zealand’s poor record of R&D expenditure. According to OECD data, in 2019 New Zealand’s spending on R&D was just 1.4% of GDP, well below the OECD average of 2.56% of GDP. Over the past 20 years research and development in spending in New Zealand has been a full percentage point of GDP below the OECD average.
So given that we also have a poor record of productivity, increasing R&D expenditure is seen as critical in improving productivity and ultimately the strength of the economy.
That’s the background behind the introduction of the loss tax credits regime. It’s intended to assist the cash flow of those companies carrying out research and development. Often in the early years, these companies are running at a loss. Hopefully once the R&D matures and bears fruit, they will then have profits resulting from the expenditure.
But funding cash flow in those early years is pretty difficult. So instead of the tax losses to be used against future profits, under the regime, companies can instead receive a payment. Note, only companies can receive this R&D tax loss credit payment. That’s because losses incurred by partnerships, limited partnerships, look-through companies and sole traders can already pass those losses through to the underlying owners anyway, who will often be able to offset them against their other income. Essentially, they are already able to benefit from the ability to cash-up losses. But companies can’t do that, hence the introduction of the regime.
By the way, this regime is not to be confused with the separate research and development tax incentive scheme, which was introduced in the 2020 tax year, again, for the same reasons to try and boost productivity.
The Inland Revenue draft interpretation statement looks at the background to scheme, summarises the rationale for scheme and how it operates. A couple of key points about the regime: you can drop in and out of it, you can opt to choose a payment in one year but not in another year. Once you have claimed a refund by cashing up your losses, the regime operates rather like an interest free loan. You’re essentially required to repay it and it’s generally treated as being repaid when the company starts paying tax, the R&D having borne fruit.
However, there are other circumstances where the credit may have to be repaid earlier when there is, in the terminology of the regime, a loss recovery event. Now, that typically will happen if there’s a disposal or transfer of the intangible property, core technology, intellectual property, etc., which is done for either less than market value or the amount sold is a non-assessable capital gain.
Another situation, and this is actually one where I’ve been involved, is where the company is no longer tax resident in New Zealand. Some very interesting issues arise in that case. Then there’s the worst-case scenario, where a company goes into liquidation although what exactly can be recovered at that point is a moot point. But that’s still a loss recovery event.
And then finally, and similar to our other rules around the carry forward of losses and imputation credits, a loss recovery may occur if there is a loss of the required shareholder continuity. In the case of the tax loss credit regime, the relevant shareholding percentage is 10%. In other words, there’s no breach if at least 10% of the voting interests of the company are held by the same group of persons throughout the relevant period.
In my view this is a very important regime for improving the future productivity of the country. The scale of the spending is going on is quite interesting to see. We can get an idea of this because the Inland Revenue as part of the budget produces what is called a tax expenditure statement.
Tax expenditure statements are a summary of the cost of a particular tax preferred regime, which, like, for example, this regime, has been introduced for specific policy reasons. The OECD collects data on tax expenditures to get a global picture of what spending is going on in tax preferred regimes.
In the case of the R&D loss tax credit, the estimated value of the expenditure for the year to 30th June 2023 is $362 million, a little bit below 1% of GDP. The estimated expenditure for the year to June 2022 was $473 million. And you can see a steady rise since the regime was introduced in 2016.
Of course, the real importance of this regime is whether it has produced a boost in total R&D spending within the economy. And then ultimately, does that lead to increased productivity. It’ll be interesting to measure these once the data flows through in due course.
So, an interesting regime and good to see Inland Revenue give some guidance on this. It contains a few hooks but it’s well worth looking at if you’re thinking about trying to make use of the scheme. And as I said, we will watch with interest to see how it bears fruit.
Shuffling forward on international Pillar One and Pillar Two proposals.
Moving on, we’ve talked fairly regularly about the OECD’s global minimum tax deal and Pillar One and Pillar Two. Last week the G20 met in India and the Secretary General of the OECD reported to the meeting that, “A historic milestone was reached at the 15th Plenary Meeting of the OECD/G20 Inclusive Framework on Base Erosion and Profit Shifting (Inclusive Framework) on 11 July 2023, as 138 members of the Inclusive Framework approved an Outcome Statement on the Two-Pillar Solution.”
In summary, what’s happened is that they’ve developed a text to a multilateral convention which will allow jurisdictions to exercise a domestic taxing right over the residual profits of the largest, most profitable multinationals. That’s what they call Amount A of Pillar One, and that will apply to multinationals with revenues in excess of €20 billion and profitability above 10%. What will happen is the scope of that taxing right will be 25% of the profit in excess of 10% of revenues. This €20 billion revenue threshold will gradually be lowered to €10 billion after seven years, conditional on the successful implementation of Amount A.
There’s a proposed framework for the simplified reporting application of arm’s length principle, which is key to transfer pricing and for baseline marketing and distribution activities. That’s what referred to as Amount B of Pillar One.
There’s a Subject to Tax Rule, again with an implementation framework, and this is really for developing countries to update their bilateral tax treaties to tax intra group income. This is where such income is subject to lower tax in another jurisdiction, in other words say one country has a 20% corporation tax rate. But that multinational shifts charges to another part of the multinational group in a jurisdiction where those charges are only taxed at a lower rate. This Subject to Tax Rule gives the first country more taxing rights in that income. Developing countries are very keen on this particular point because they feel that this is where the current tax regime has been almost predatory on their tax base.
There will be a comprehensive action plan developed by the OECD to “Support the swift and coordinated implementation of the Two Pillar Solution, coordinating with regional and international organisations”
On the face of it, all pretty much good news. But it’s interesting to read the views of those people who specialise in this field and there still seems to be quite a bit of uncertainty about whether in fact this whole thing will come to fruit.
In the meantime, for example, you’ve got lobbying going on in the United States. And it appears now that the US has managed to secure a further delay in the implementation of the Pillar Two global minimum tax 15% until 2026, according to a report coming out of the United States.
Pillar Two is the key proposal, because it applies to companies with annual revenues in excess of €750 million. Apparently, the US Treasury Department has managed to negotiate a delay in the implementation of this. It has got people watching all around the world as to what’s going on. It also means that the in the background, digital services taxes, for example, could still be ready to be deployed or introduced by jurisdictions if they feel that Pillar Two isn’t making enough progress and they want to secure their revenues. [Under the agreement just announced countries have agreed to hold off imposing “newly enacted” digital services taxes until after 31st December 2024.]
Overall, it’s a bit of a shuffling: one step forward, maybe half a step sideways and a quarter of a step back. In other words, progress is slow, but it’s still inching the way forward. Ultimately, it comes down to watching what happens in the United States and the lobbying goes on. If there’s a change of President next year all bets will be off at that point, I would say.
Smith, banged to rights, again. But should Companies Office be in the gun?
And finally, this week, the murderer and escapee, Philip John Smith, who’s been in jail since 1995 apart from the brief time he escaped to Brazil has now been sentenced to further two years imprisonment on tax fraud charges.
He was convicted for dishonestly using documents intending to gain pecuniary advantage, firstly, a application under the Small Business Cashflow Scheme and then for filing 17 false GST returns and a false income tax return. in total the attempted fraud was just over $66,000 of which was actually paid $53,593. He’s also been ordered to pay full reparations on that amount.
What he did was between October 2019 and March 2020, he registered five companies with the Companies Office with shareholders and directors, who were friends, associates or third parties unknown to him. He then he set up and activated myIR accounts for each company.
But Inland Revenue was quite quickly onto him, it seems, because it apparently detected the fraud involving the Small Business Cashflow Scheme in June 2020 only a few months after it started operating in April. So good quick work by Inland Revenue.
But the case also raises the point which an associate I bumped into this week mentioned, and that’s the actions (or inaction) of the Companies Office in allowing those five companies to get set up. New Zealand scores highly for ease of business in establishing companies. Many times, whenever I’m talking to overseas people, they are remarkably impressed about how quick it is to set up a company in New Zealand.
The question arises if people setting up companies by going directly through the Companies Office website, is it a little bit too easy? Was an opportunity to pick up Smith’s attempted fraud missed at that point by Companies Office? We don’t know. Accountants and lawyers are subject to the current anti-money laundering legislation, so we need to pay attention to what’s going on with company registrations and we have to obtain proof of ID. But my understanding is this process is a little less rigorous when you go directly through the Companies Office.
So good work by Inland Revenue picking it up quickly and catching Smith, again. But maybe some questions should be asked as to whether he should ever have been able to get that far along the line and that Companies Office should have picked it up sooner.
And finally, congratulations to the Football Ferns for their magnificent win last night at the start of the FIFA Women’s World Cup. I was lucky enough to be at Eden Park, which is why I might sound a little hoarse today! It was fantastic to experience such a great occasion even if the final nine minutes seemed like an hour. Congratulations again to everyone involved. Football definitely was the winner on the night!
That’s all for this week. I’m Terry Baucher and you can find this podcast on my website www.baucher.tax or wherever you get your podcasts. Thank you for listening and please send me your feedback and tell your friends and clients. Until next time, kia pai to rā. Have a great day.

